More than a year ago, I stumbled upon a fun article published in the Stanford Social Innovation Review (SSIR) titled “Ten Nonprofit Funding Models“. It provided clarity for me around what I was seeing in the non-profit sector. So, I bookmarked it and re-read it from time-to-time. Recently, I’ve found myself talking to a number of different non-profit professionals and board volunteers about this article, which is usually a sure sign that I better blog about it.
More than a year ago, I stumbled upon a fun article published in the Stanford Social Innovation Review (SSIR) titled “Ten Nonprofit Funding Models“. It provided clarity for me around what I was seeing in the non-profit sector. So, I bookmarked it and re-read it from time-to-time. Recently, I’ve found myself talking to a number of different non-profit professionals and board volunteers about this article, which is usually a sure sign that I better blog about it.
As you know, there are many different types of organizations calling themselves members of the non-profit sector.
- Churches
- Universities
- Hospitals
- Arts organizations
- Membership organizations (e.g. chamber of commerce, etc)
- Human Services/Social Services
Each of these types of non-profit organizations look very different. Each board has different wrinkles, and their revenue models also take on a different complexion.
The SSIR article by William Landes Foster, Peter Kim, & Barbara Christiansen names and describes ten different funding models:
- Heartfelt Connector
- Beneficiary Builder
- Member Motivator
- Big Bettor
- Public Provider
- Policy Innovator
- Beneficiary Broker
- Resource Recycler
- Market Maker
- Local Nationalizer
Some of you are probably wondering what each of these models means. I encourage you to click-through to the SSIR article and read it for yourself. Those authors do a great job of breaking down each of the models.
What I’ve found myself talking to many non-profit professionals and board members about lately isn’t which revenue model they’re using. My conversations have been rooted in what the authors of this article say in their final few paragraphs:
“In the current economic climate it is tempting for nonprofit leaders to seek money wherever they can find it, causing some nonprofits to veer off course. That would be a mistake. During tough times it is more important than ever for nonprofit leaders to examine their funding strategy closely and to be disciplined about the way that they raise money. We hope that this article provides a framework for nonprofit leaders to do just that.”
In my opinion, it is so true that many non-profit organizations have sought money wherever they can find it, especially once they realized that the economy isn’t going to just snap back into place and we now find ourselves in a “New Normal”.
 So, the conversations I’ve been referencing throughout this post have to do with board development and not the actual revenue models.
So, the conversations I’ve been referencing throughout this post have to do with board development and not the actual revenue models.
I believe that non-profit organizations build their boards around their revenue model. For example, if your agency is highly dependent on fees, then you probably haven’t recruited world-class fundraising volunteers to sit on your board. The same holds true for organizations with a government funding revenue model.
So, when you start tinkering with your revenue model (e.g. adding an event, pledge drive, direct mail, etc), I believe it creates tension in the boardroom for two reasons:
- You’re asking people to do something that wasn’t part of the original deal.
- You’re also asking people to do something they aren’t likely good at doing.
If you find yourself in the position of having to tweak your revenue model, I suggest the following:
- Facilitate a conversation in the boardroom and build consensus around the idea of changing or tweaking your revenue model. Make sure all consequences are understood and appreciated.
- Ask your board governance committee to complete a new gap assessment based upon some of the new roles you’re asking board members to take on.
- Focus your board recruitment efforts on bringing in new board volunteers to help fill your newly identified gaps.
- Allow current board members to step off the board gracefully and help them find a new seat on the bus where they can still participate in your mission.
- If you need a blended board to make your blended revenue model work, then deliberately talk about roles and responsibilities in the board room to avoid misunderstandings between volunteers.
The New Normal may have thrown your organization a curveball, but it doesn’t mean you need to go through a dysfunctional transition. A little bit of thoughtfulness and board engagement can go a long way.
Did you click-through and read the Stanford Social Innovation Review article? If so, what were your thoughts? Which revenue model is your agency using? Do you find yourself tweaking your revenue model in an effort to adapt to The New Normal? How is your board handling the transition?
Please scroll down and share your thoughts and observations in the comment box below. We can all learn from each other.
Here’s to your health!
Erik Anderson
Founder & President, The Healthy Non-Profit LLC
www.thehealthynonprofit.com
erik@thehealthynonprofit.com
http://twitter.com/#!/eanderson847
http://www.facebook.com/eanderson847
http://www.linkedin.com/in/erikanderson847

 Welcome to O.D. Fridays at DonorDreams blog. Every Friday for the foreseeable future we will be looking at posts from John Greco’s blog called “
Welcome to O.D. Fridays at DonorDreams blog. Every Friday for the foreseeable future we will be looking at posts from John Greco’s blog called “ Do you see it? Culture eats strategy!
Do you see it? Culture eats strategy! Hmmmm … looking back at that meeting, I think he was cooking up a hearty breakfast for me.
Hmmmm … looking back at that meeting, I think he was cooking up a hearty breakfast for me.
 Once your hire an Executive Director, s/he needs to be supported. Supporting an Executive Director is where the rubber meets the road.
Once your hire an Executive Director, s/he needs to be supported. Supporting an Executive Director is where the rubber meets the road.

 These five bullet points are just the tip of the iceberg. The fact of the matter is that we started planning next year’s Duck Race in the immediate days and weeks after wrapping one up. This special event raffle was a year-round affair.
These five bullet points are just the tip of the iceberg. The fact of the matter is that we started planning next year’s Duck Race in the immediate days and weeks after wrapping one up. This special event raffle was a year-round affair.
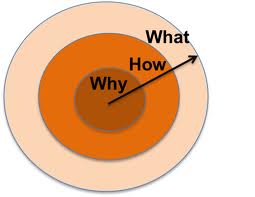 Those organizations that excel at strategic planning have a very clear understanding of what they do, how they do it, and why they exist. However, those organizations that are little fuzzy on these ideas do a lot of wrestling with themselves. Sometimes countless hours are spent at the 50,000 foot view talking about these issues . . . and for good reason! Without clarity on What-How-Why, there is no way you can set goals, develop objectives and write action plans that are meaningful in any way, shape or form.
Those organizations that excel at strategic planning have a very clear understanding of what they do, how they do it, and why they exist. However, those organizations that are little fuzzy on these ideas do a lot of wrestling with themselves. Sometimes countless hours are spent at the 50,000 foot view talking about these issues . . . and for good reason! Without clarity on What-How-Why, there is no way you can set goals, develop objectives and write action plans that are meaningful in any way, shape or form. When I used to work at Boys & Girls Clubs of America (BGCA), my colleagues were responsible for the existence of something called theFUNDRAI$INGbank, which is a special webpage embedded inside of the intranet accessible to local affiliates. We outsourced maintenance of this page to FundRaisingInfo.com. There were many different resources located on “The Bank” including a free service called “Ask The Expert“.
When I used to work at Boys & Girls Clubs of America (BGCA), my colleagues were responsible for the existence of something called theFUNDRAI$INGbank, which is a special webpage embedded inside of the intranet accessible to local affiliates. We outsourced maintenance of this page to FundRaisingInfo.com. There were many different resources located on “The Bank” including a free service called “Ask The Expert“.
 September 15, 2008 . . . do you remember where you were and what you were doing? It was the day the world changed. It was what some people have called an “economic 9-11″. Regardless of how you characterize the day that Lehman Brothers filed for bankruptcy and the stock market started its crash, it is hard to argue the following: 1) the economic paradigm we all used to live in shifted and 2) nothing will ever be the same again.
September 15, 2008 . . . do you remember where you were and what you were doing? It was the day the world changed. It was what some people have called an “economic 9-11″. Regardless of how you characterize the day that Lehman Brothers filed for bankruptcy and the stock market started its crash, it is hard to argue the following: 1) the economic paradigm we all used to live in shifted and 2) nothing will ever be the same again. Mentally take a look around your board room and see if you can identify how many Dorothy-like volunteers occupy chairs. They are kind folks (dare I say friends) who look and sound like the following:
Mentally take a look around your board room and see if you can identify how many Dorothy-like volunteers occupy chairs. They are kind folks (dare I say friends) who look and sound like the following: Don’t get me wrong. I am not suggesting a “witch hunt” to root out these folks and fire them. Dorothy serves an important role on your board. She is that cautious voice that keeps you from getting into trouble. She will stop you from pulling the plug on your annual campaign and direct mail appeals and “going all in” on ePhilanthropy efforts. Valuable? YES! However, what happens when you have too many Dorothy-like board members? Or what if you have those well-intentioned people serving in the wrong roles (e.g. board president, annual campaign chair, strategic planning committee, etc)?
Don’t get me wrong. I am not suggesting a “witch hunt” to root out these folks and fire them. Dorothy serves an important role on your board. She is that cautious voice that keeps you from getting into trouble. She will stop you from pulling the plug on your annual campaign and direct mail appeals and “going all in” on ePhilanthropy efforts. Valuable? YES! However, what happens when you have too many Dorothy-like board members? Or what if you have those well-intentioned people serving in the wrong roles (e.g. board president, annual campaign chair, strategic planning committee, etc)? Last month I wrote on post entitled
Last month I wrote on post entitled  The alternative is this with the same beginning:
The alternative is this with the same beginning: Here’s the rub . . . Board strength isn’t just an internal issue that is invisible to the community. It is visible. Here’s what it looks like:
Here’s the rub . . . Board strength isn’t just an internal issue that is invisible to the community. It is visible. Here’s what it looks like: