Dani Robbins is the Founder & Principal Strategist at Non Profit Evolution located in Columbus, Ohio. I’ve invited my good friend and fellow non-profit consultant to the first Wednesday of each month about board development related topics. Dani also recently co-authored a book titled “Innovative Leadership Workbook for Nonprofit Executives” that you can find on Amazon.com.
Governance: The Work of the Board, part 4
Raising Money
By Dani Robbins
 Welcome to part four of our five part series on Governance. We have already discussed the Board’s role in Hiring, Supporting and Evaluating the Executive, Acting as the Fiduciary Responsible Agent, and Setting Policy. Today, let’s discuss the Board’s role in raising money.
Welcome to part four of our five part series on Governance. We have already discussed the Board’s role in Hiring, Supporting and Evaluating the Executive, Acting as the Fiduciary Responsible Agent, and Setting Policy. Today, let’s discuss the Board’s role in raising money.
As previously mentioned, Boards are made up of appointed community leaders who are collectively responsible for governing an organization. As outlined in my favorite Board book Governance as Leadership and summarized in The Role of the Board, the Fiduciary Mode is where governance begins for all boards and ends for too many. I encourage you to also explore the Strategic and Generative Modes of Governance, which will greatly improve your board’s engagement, and also their enjoyment.
At a minimum, governance includes:
- Setting the Mission, Vision and Strategic Plan
- Hiring, Supporting and Evaluating the Executive Director
- Acting as the Fiduciary Responsible Agent
- Raising Money and
- Setting Policy
One of my goals for this blog is to rectify the common practice in the field of people telling nonprofit executives and boards how things should be done without any instruction as to what that actually means or how to accomplish it.
What “Board members being responsible for raising money” means is:
The Board sets the fund raising (also called resource development) goal; embarks on the campaign; opens doors; introduces staff; “makes the ask” when they’re the most likely person to get a yes (regardless of title or ranking, you always send the person who is most likely to get a yes to a gift request); picks up the tab for lunch when possible; and thanks the donor. The Board is also responsible for setting the strategic plan which may include a goal to increase contributed income. Each Board member should be expected to make a significant gift, reflective of their personal circumstances, as well as raise additional money.
I do not recommend give or get policies.
Give or get policies allow Board members to avoid personally giving; and 100% Board giving is critical for a successful campaign. Potential donors will ask if there is 100% Board giving, and the answer must be “yes“. Why should anyone else support an organization whose Board members do not? Moreover, how can you ask for someone else to financially support an organization you do not financially support? I can hear someone out there saying “I give of my time,” and that is wonderful, but it’s not enough. Board members should also financially support the organizations they serve.
I also don’t recommend set giving requirements.
Set giving policies, intended to be minimum gifts, actually end up being the entire gift. Such policies alienate potential board members who may bring a lot to the table but cannot personally give at the set level. It also leaves money on the table for people who can give more. Finally, it eliminates the Resource Development Committee’s opportunity to seek out and personally ask each Board member for a specific (to their circumstances and level of engagement) gift. It takes away the chance to say thank you for your engagement, removes the possibility to steward Board members as donors and minimizes the chance of a larger gift. Any policy that works against your goals is not a good policy.
The Board cannot and is not expected to raise money alone.
The staff is responsible for training the Board; coordinating the assignments; preparing the askers with relevant donor information; drafting and supplying whatever written information will be left with the donor, including a case statement (also called case for support) and a letter asking for a specific dollar amount; attending the ask meetings as appropriate; documenting the meeting in the database; writing the formal thank you note; and creating a plan to steward (or circle back to) the donor going forward.
The executive director cannot raise money alone. The development director cannot raise money alone. Fundraising works best in a culture of philanthropy when both the staff and the Board are working together to increase contributed income.
What’s been your experience? As always, I welcome your insight and experience.


 Welcome to O.D. Fridays at DonorDreams blog. Every Friday for the foreseeable future we will be looking at posts from John Greco’s blog called “
Welcome to O.D. Fridays at DonorDreams blog. Every Friday for the foreseeable future we will be looking at posts from John Greco’s blog called “ I find this distinction really fascinating, and I haven’t been able to stop thinking about it since I read this post. So, I’ve been focused on identifying some non-profit related “predicaments” and here is what I’ve come up with . . .
I find this distinction really fascinating, and I haven’t been able to stop thinking about it since I read this post. So, I’ve been focused on identifying some non-profit related “predicaments” and here is what I’ve come up with . . . Board member engagement is a common thread running through many of my blog posts. This isn’t because I’m a broken record. The fact of the matter is that so many of the things that plague non-profits are simply “symptoms” of a bigger problem. Yep, you guessed it . . . the root cause of many of our challenges in the can be traced back to our boards.
Board member engagement is a common thread running through many of my blog posts. This isn’t because I’m a broken record. The fact of the matter is that so many of the things that plague non-profits are simply “symptoms” of a bigger problem. Yep, you guessed it . . . the root cause of many of our challenges in the can be traced back to our boards. Last week a dear non-profit friend of mine from California couldn’t sleep. She tossed and she turned. Ultimately, she got out of bed, turned on her computer and started talking into a microphone. When I woke up in the morning in my bed in Elgin, Illinois, there was an email sitting in my inbox with a voice file attachment. Her words have tumbled around in my head for a week, and I’ve decided to enlist your support in dissecting them.
Last week a dear non-profit friend of mine from California couldn’t sleep. She tossed and she turned. Ultimately, she got out of bed, turned on her computer and started talking into a microphone. When I woke up in the morning in my bed in Elgin, Illinois, there was an email sitting in my inbox with a voice file attachment. Her words have tumbled around in my head for a week, and I’ve decided to enlist your support in dissecting them. After listening to my friend’s recording, I started Googling around and searching for anything that anyone might have written about characteristics and traits of effective boards. I was especially intrigued by her question about incorporating personality testing into the board development process. After all, many workplaces are incorporating this type of assessment into their employee hiring process.
After listening to my friend’s recording, I started Googling around and searching for anything that anyone might have written about characteristics and traits of effective boards. I was especially intrigued by her question about incorporating personality testing into the board development process. After all, many workplaces are incorporating this type of assessment into their employee hiring process. Competencies
Competencies When I engage non-profit organizations in board development related issues, it can be like simultaneously operating in two parallel and polar opposite universes. One universe exists where everyone is talking about how things are “supposed to be” done. This is described in the agency’s written board development plan. In the other universe, there are board members and staff sitting around a table talking about “some guy” they know without any discussion about board composition gap assessment, prospect lists, prospect evaluation or anything that sounds like process.
When I engage non-profit organizations in board development related issues, it can be like simultaneously operating in two parallel and polar opposite universes. One universe exists where everyone is talking about how things are “supposed to be” done. This is described in the agency’s written board development plan. In the other universe, there are board members and staff sitting around a table talking about “some guy” they know without any discussion about board composition gap assessment, prospect lists, prospect evaluation or anything that sounds like process. With this in mind, I am reminded of an old “Mondays with Marissa” post from a year ago titled “
With this in mind, I am reminded of an old “Mondays with Marissa” post from a year ago titled “ More than a year ago, I stumbled upon a fun article published in the Stanford Social Innovation Review (SSIR) titled “
More than a year ago, I stumbled upon a fun article published in the Stanford Social Innovation Review (SSIR) titled “ So, the conversations I’ve been referencing throughout this post have to do with board development and not the actual revenue models.
So, the conversations I’ve been referencing throughout this post have to do with board development and not the actual revenue models. Welcome to O.D. Fridays at DonorDreams blog. Every Friday for the foreseeable future we will be looking at posts from John Greco’s blog called “
Welcome to O.D. Fridays at DonorDreams blog. Every Friday for the foreseeable future we will be looking at posts from John Greco’s blog called “ Do you see it? Culture eats strategy!
Do you see it? Culture eats strategy! Hmmmm … looking back at that meeting, I think he was cooking up a hearty breakfast for me.
Hmmmm … looking back at that meeting, I think he was cooking up a hearty breakfast for me. Welcome to part three of our five-part series on Governance. We have already discussed the Board’s role in
Welcome to part three of our five-part series on Governance. We have already discussed the Board’s role in  I recommend organizations have the following policies:
I recommend organizations have the following policies: Policies address today. Plans take you into the future.
Policies address today. Plans take you into the future.
 The audit is prepared by an independent accounting firm in an effort to assess if the organization is operating in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and also within their commitments. Different audits are required based on the amount of government funding that is received. The costs of such audits vary depending on the budget size, revenue streams, and also the quality of the financial systems and the need to for the auditor to clean up those systems.
The audit is prepared by an independent accounting firm in an effort to assess if the organization is operating in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and also within their commitments. Different audits are required based on the amount of government funding that is received. The costs of such audits vary depending on the budget size, revenue streams, and also the quality of the financial systems and the need to for the auditor to clean up those systems.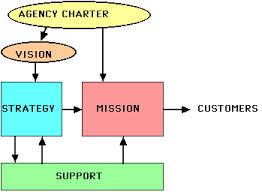 Finally, as part of meeting their fiduciary responsibility, the Board should understand how the programs tie to the mission, the number of people served in those programs as well as the impact of that program.
Finally, as part of meeting their fiduciary responsibility, the Board should understand how the programs tie to the mission, the number of people served in those programs as well as the impact of that program.
 Once your hire an Executive Director, s/he needs to be supported. Supporting an Executive Director is where the rubber meets the road.
Once your hire an Executive Director, s/he needs to be supported. Supporting an Executive Director is where the rubber meets the road.